AMAZING COUNTRIES

ART IN INDIA
| Art in Russia |
|
Indian paintings provide an aesthetic continuum that extends from the early civilization to the present day. This form of art in India is vivid and lively, refined and sophisticated and bold and vigorous at the same time.
|
|||||||||||
MURALS
|
||||||||||||
MINIATURES
'Miniature' generally refers to a painting or illumination, small in size meticulous in detail and delicate in brushwork. |
||||||||||||
FOLK PAINTING
|
||||||||||||
MYSORE PAINTING
|
||||||||||||
MADHUBANI PAINTING
|
||||||||||||
TANJORE PAINTING
|
||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||
Embroidery is the art or handicraft of decorating fabric or other materials with needle and thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as metal strips, pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. Embroidery is most often recommended for caps, hats, coats, blankets, dress shirts, denim, stockings, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available with a wide variety of thread or yarn colour .
|
||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||
PHULKARI Phulkari from the Punjab region of India. Phulkari embroidery, popular since at least the 15th century, is traditionally done on hand-spun cotton cloth with simple darning stitches using silk floss |
||||||||||||
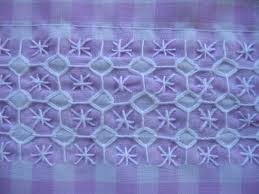
CHICKEN Chicken scratch is an easy type of embroidery done on gingham(checkered) fabric, which gives the impression of appliquéd lace |
 |
|||||||||||
ZARDOZI
|
 |
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
HAWA MAHAL Hawa Mahal stands upright as the entrance to the City Palace, Jaipur. An important landmark in the city, Hawa Mahal is an epitome of the Rajputana architecture. The splendid five-storey “Palace of the Winds” is a blend of beauty and splendor much close to Rajasthan’s culture. Maharaja Sawai Pratap Singh built Hawa Mahal in 1779. The pyramid shape of this ancient monument is a tourist attraction having 953 small windows. |
 |
|||||||||||
TAJ MAHAL Taj Mahal, the pinnacle of Mughal architecture, was built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (1628-1658), grandson of Akbar the great, in the memory of his queen Arjumand Bano Begum, entitled ‘Mumtaz Mahal’. Mumtaz Mahal was a niece of empress Nur Jahan and granddaughter of Mirza Ghias Beg I’timad-ud-Daula, wazir of emperor Jehangir. She was born in 1593 and died in 1631, during the birth of her fourteenth child at Burhanpur. Her mortal remains were temporarily buried in the Zainabad garden. Six months later, her body was transferred to Agra to be finally enshrined in the crypt of the main tomb of the Taj Mahal. The Taj Mahal is the mausoleum of both Mumtaz Mahal and Shah Jahan. |
 |
|||||||||||
CHARMINAR The charminar Hyderabad’s best known landmark was built 1591 by Sultan Mohammed Quli Qutub Shah to appease the force of evil savaging his new city with epidemic and plague. Standing in the heart of the old walled city and surround by lively bazaars, the charminar (‘four tower’) is a 56m high triumphal arch. The arch is notable for its elegant balconies, stucco decorations and the small mosque, Hyderabad’s oldest, on the 2nd floor. An image of the grace every packet of charminar cigarettes, one of India’s most popular brand. |
 |
|||||||||||
BULAND DARWAZA Buland Darwaza meaning 'high' or 'great' gate in Persian, is a monument that can be found in Fatehpur Sikri which is located 43kms away from Agra, India. The construction of this city began in about 1569 and was completed in 1584. The architectural style of these buildings has Persian influence. The various buildings found here are- Jodha Bai palace, Birbal's palace, Panch Mahal etc. Buland Darwaza is one of them.It is known as the "Gate of Magnificence". It was built by Akbar in 1602 to commemorate his conquest of Gujarat. The gateway is approached by 42 steps. It is about 40 metres high. It is built of red sandstone and inlaying of white marble. There is an inscription one on the monument which is a message from Jesus advising his followers not to consider this world as their permanent home. |
 |
|||||||||||
GOLDEN TEMPLEThe Golder Temple (Harmandir Sahib/Darbar Sahib), is the holiest shrine of Sikhism. Guru Ram Das Ji founded the city of Amritsar in the 16th century when it was constructed. An active place of worship for Sikhs, the Harmandir Sahib is also visited by people from other religion. |
 |
|||||||||||
SANCHI STUPAThe Great Stupa at Sanchi was built by the emperor Ashoka the Great in the 3rd century BC. Its nucleus was a simple hemispherical brick structure built over the relics of the Buddha. |
 |
|||||||||||







